44+ The Anatomy Of Hip Joint. Related online courses on physioplus. The clinician must be familiar with the normal embryological, anatomical and biomechanical features of the hip joint.
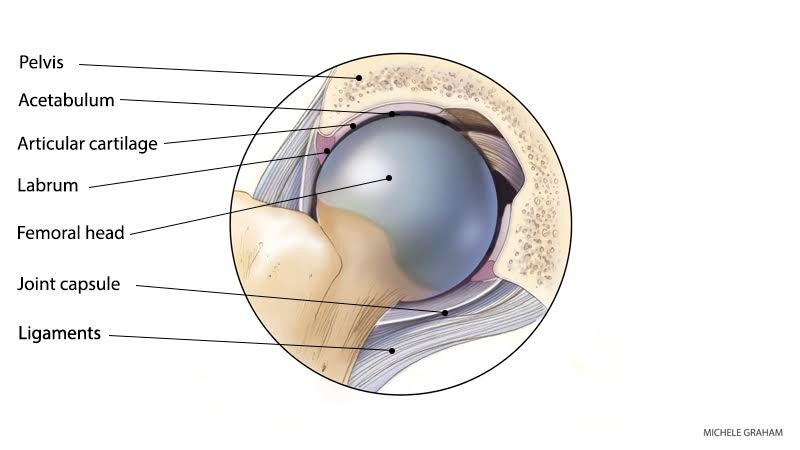
Understanding how the different layers of the hip are built and connected can help you understand how the hip works, how it can be injured, and how challenging recovery can be when this joint is injured.
The transverse acetabular ligament (latin: Hip joint is an articulation between the femoral head and the acetabulum of the hip bone. The acetabulum is a concave area in the pelvis, into which the femoral head fits. The muscles involved in hip motion are attached to the joint at these trochanters.